Table of Contents
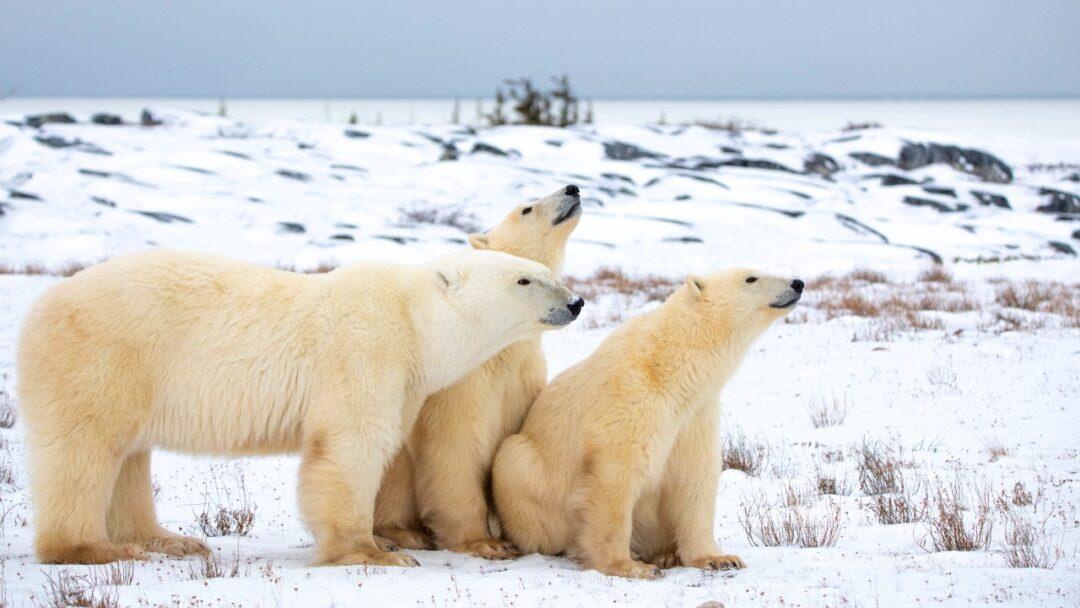

Introduction
The Remarkable Adaptations of Arctic Animals. The Arctic is a harsh environment that presents many difficulties for life because of its icy landscapes and piercingly cold temperatures. But despite all the odds, a fascinating variety of animals have developed extraordinary adaptations that enable them to survive in this hostile environment. These hardy animals, which range from majestic polar bears to elusive Arctic foxes, have a diverse array of means of surviving. In this article, we’ll explore the extraordinary adaptations that allow Arctic animals to withstand extreme cold, traverse perilous terrain, and find food amidst the constant hardships of their frozen home.
Polar Bears: Masters of the Ice
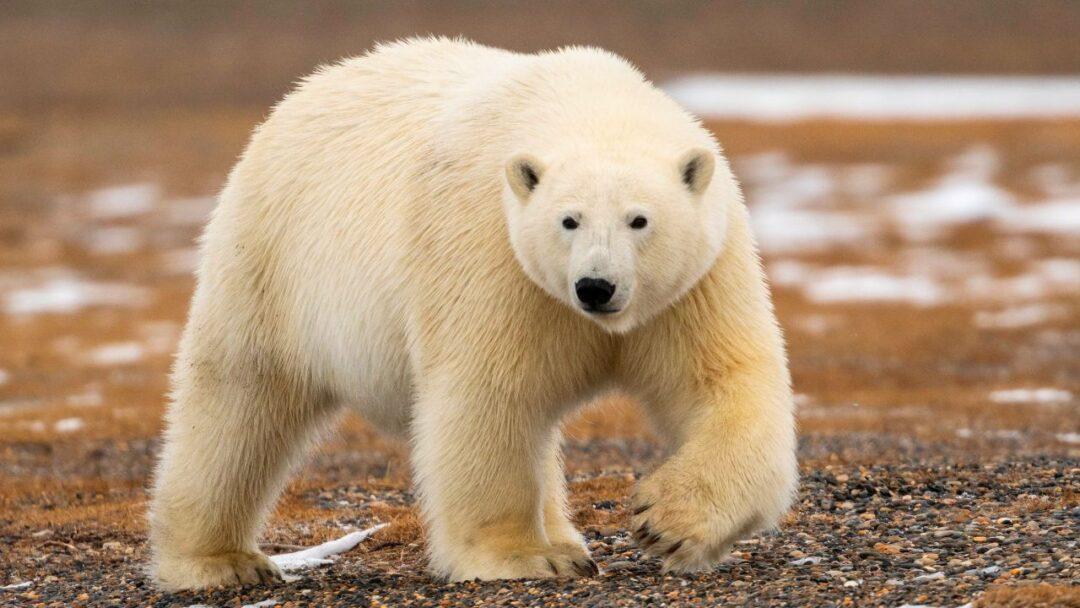

The undisputed rulers of the Arctic, polar bears are ideally adapted to live in this harsh environment. The combination of their enormous size, strong paws, and insulating fur makes them fearsome predators. Polar bears have excellent thermal insulation thanks to their thick layer of blubber and hollow hair shafts that trap heat. Their dark skin efficiently absorbs the sun’s rays and transforms them into heat. These adaptations enable them to travel great distances across ice floes in search of seals, their main prey, as well as having excellent swimming skills and a keen sense of smell.
Arctic Foxes: Camouflaged Survivors
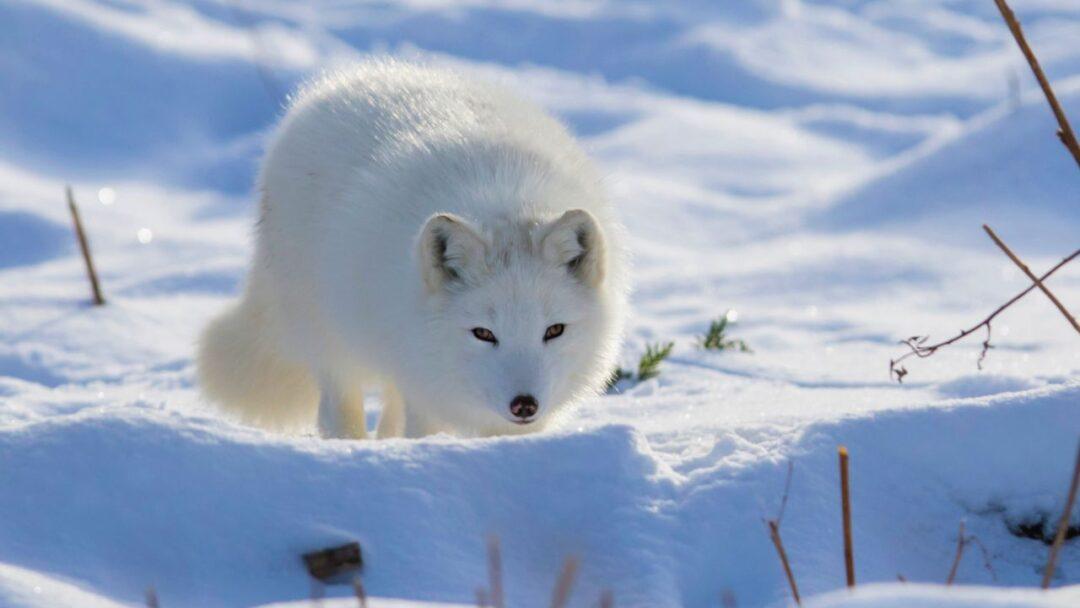

Arctic foxes, which are distinguished by their beautiful white coats, have developed a special survival technique to deal with the harsh Arctic environment. Their dazzling white winter fur acts as camouflage against the snow during the colder months. Their coat changes to a brown or gray color in the summer, blending in perfectly with the tones of the tundra. Due to these adaptations, Arctic foxes can stalk their prey—most commonly lemmings and small rodents—covertly. They also have small bodies and furry paws that act as natural snowshoes for quick movements over icy terrain.
Walruses: Rugged Giants of the Arctic Seas
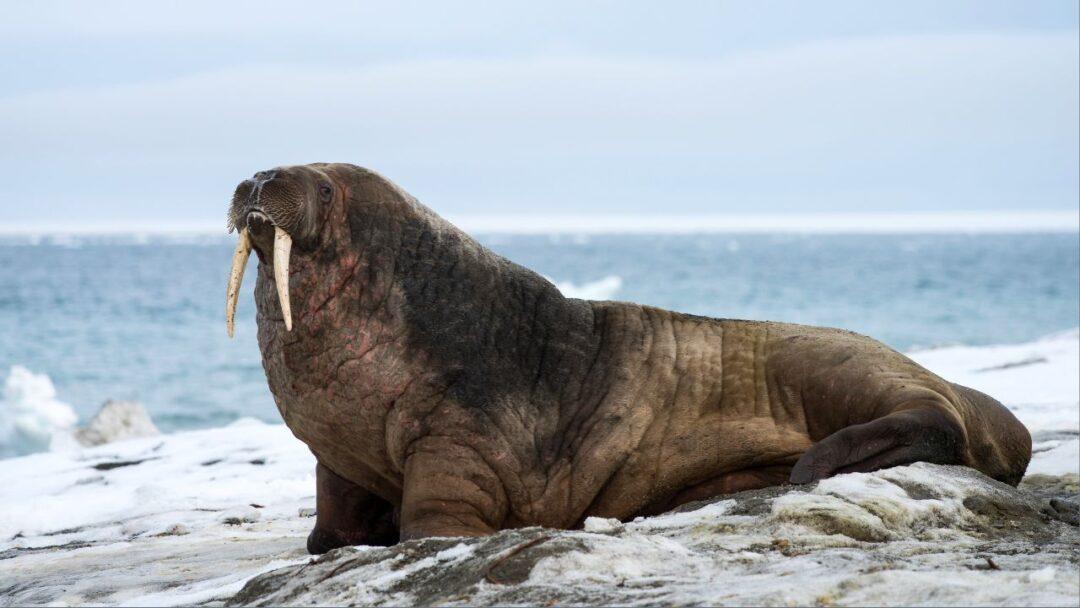

Walruses are well-adapted to withstand the harsh Arctic environment thanks to their enormous tusks and sturdy bodies. These impressive animals fight other males during breeding season and haul themselves onto ice floes using their long ivory tusks, among other things. When food is in short supply, their thick layer of blubber acts as insulation, buoyancy, and a valuable energy reserve. Additionally, while diving to great depths in search of mollusks and other benthic organisms, walruses have a remarkable capacity to conserve oxygen.
Narwhals: The Unicorns of the Sea
The icy waters of the Arctic are home to narwhals, which are frequently referred to as the sea’s unicorns. Their elongated tusk, which is actually a modified tooth, is their most amazing adaptation. Although the function of this tusk is still up for debate, it probably has a variety of uses, such as mating rituals and as a sensory organ. Narwhals use their tusks to sense changes in water temperature, salinity, and prey as they move through small channels in the ice. They can find food, primarily fish and squid, thanks to their streamlined bodies and capacity to dive to great depths.
Seals: Agile Swimmers and Ice Experts

Bearded seals and ringed seals, for example, are true masters of their Arctic habitat. Their webbed feet and streamlined bodies allow them to move through icy waters with amazing agility. In order to access the air while avoiding predators, seals have the extraordinary ability to create and maintain breathing holes in the ice. These resourceful marine mammals are able to locate and detect their prey, which is primarily fish and crustaceans, beneath the ice because they have developed specialized vision.
How do Arctic animals survive in such cold conditions?
Arctic animals have a variety of adaptations that enable them to endure the bitter cold. They have dense fur or feathers and thick layers of insulating fat that offer excellent insulation. Additionally, some have heat-retaining blood circulation systems. Additionally, because of their small surface areas and compact body shapes, they lose less heat. Some species, like the polar bear, have insulation-enhancing adaptations like a thick layer of blubber and hollow fur.
How do Arctic animals find food in such a harsh environment?
Animals in the arctic use a variety of methods to find food in their difficult environment. To find seals and other prey, some animals, like the polar bear, use hunting strategies and their keen sense of smell. Others, like the Arctic fox, can scavenge, hunt small mammals, or consume berries, and their diets change according to what is available. The walrus is one marine mammal that consumes benthic organisms from the seafloor.
How do Arctic animals stay warm underwater?
Arctic animals with a preference for the chilly waters have unique thermal adaptations. The thick layer of blubber that marine mammals like seals, whales, and walruses have serves as insulation and aids in heat retention. Additionally, when they dive, their blood vessels constrict, rerouting blood flow to crucial organs and preserving heat. In order to reduce heat loss, some animals have thick coats of fur or skin modifications.
How do Arctic animals cope with long periods of darkness during winter?
Arctic animals have special strategies for dealing with prolonged darkness. Some species, like the Arctic hare, can disguise themselves from predators by altering the color of their fur to blend in with the surrounding snow. Others, like the Arctic wolf, can hunt and navigate in low light thanks to their excellent night vision. Lemmings are among the animals that go through behavioral and physiological changes to adjust their activity patterns to the dark.
How do Arctic animals deal with the melting ice and changing climate?
Animals in the Arctic face difficulties as a result of melting ice and climate change. For instance, polar bears depend on sea ice to hunt seals, and their ability to do so is negatively impacted by ice loss. Some creatures, such as the Arctic fox, face competition from southern species that are migrating north. In general, Arctic animals are under pressure to adapt to new conditions or face difficulties in surviving due to the changing climate.
Conclusion
The Arctic pushes the boundaries of survival due to its icy expanse and harsh environment. Yet the astounding resilience of life on our planet is attested to by the remarkable adaptations shown by Arctic animals. Each species, from the majestic polar bears to the elusive narwhals, has developed a special set of abilities and behaviors to withstand the extreme cold, negotiate perilous terrain, and find food in one of the harshest environments on Earth. Understanding these adaptations not only highlights the wonders of nature but also emphasizes how crucial it is to protect and preserve these delicate Arctic ecosystems so that future generations can observe and enjoy them.
VOLCANOES: FORCES OF NATURE AND GEOLOGICAL WONDERS : NEXT POST




